Athletic Foot
The Problem
 Athlete’s foot — also called tinea pedis — is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin of the webs of the toes and soles of the feet. It commonly occurs in people whose feet have become very sweaty while confined within tightfitting shoes.
Athlete’s foot — also called tinea pedis — is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin of the webs of the toes and soles of the feet. It commonly occurs in people whose feet have become very sweaty while confined within tightfitting shoes.
Athlete’s foot isn’t serious, but sometimes it’s hard to cure. However, if you have diabetes or a weakened immune system and suspect that you have athlete’s foot, you should call your doctor immediately.
Factors that increase your risk of getting athlete’s foot include:
- visiting public places barefoot, especially locker rooms, showers, and swimming pools
- sharing socks, shoes, or towels with an infected person
- wearing tight-fitting, closed-toe shoes
- keeping your feet wet for long periods of time
- having sweaty feet
- having a minor skin or nail injury on your foot
Signs and symptoms of athlete’s foot include a scaly rash that usually causes itching, stinging and burning. Athlete’s foot is contagious and can be spread via contaminated floors, towels or clothing.
Treatment
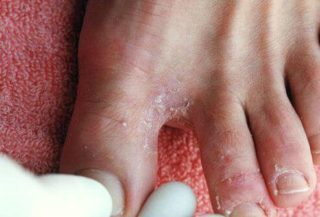 Treatment athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) depends on its type and severity. Most cases of athlete’s foot can be treated at home using an antifungal medicine to kill the fungus or slow its growth. If the treatment doesn’t respond, you may need a prescription-strength medication to apply to your feet. Severe infections may require antifungal pills that you take by mouth.
Treatment athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) depends on its type and severity. Most cases of athlete’s foot can be treated at home using an antifungal medicine to kill the fungus or slow its growth. If the treatment doesn’t respond, you may need a prescription-strength medication to apply to your feet. Severe infections may require antifungal pills that you take by mouth.
There are a lot of treatments available at Dr. foot for fungal infections which include everything from over the counter creams, right through to prescription medications.
- Topical treatments. Topical creams and sprays can relieve mild cases of athlete’s foot. However, if the skin on the sole of your foot is tough or thickened, topical treatments might not be able to penetrate it.In addition, over-the-counter preparations typically contain very low doses of the drug intended to get rid of the fungus, whereas your podiatrist can usually prescribe a stronger treatment.
- Oral prescriptions. If your athlete’s foot persists despite topical treatment, you might need an oral antifungal medicine to eliminate the infection.
- At-home treatments. Soaking your feet in vinegar or other home remedies might relieve the symptoms of athlete’s foot; however, they might not stop a chronic case from coming back.
A cleansing regimen. A good podiatrist will discuss how to keep future infections at bay through lifestyle changes, such as keeping your feet clean and dry on a daily basis.


